RSS Error: A feed could not be found at `https://rss.app/feeds/KD843mj8YEDbLDRX.xml`; the status code is `402` and content-type is `text/plain; charset=utf-8`
RSS Error: A feed could not be found at `https://rss.app/feeds/ntzUwlR6zaTflwXQ.xml`; the status code is `402` and content-type is `text/plain; charset=utf-8`

CBD and CBG may help the liver recharge and clean itself—offering a promising new plant-based strategy against fatty liver disease. Scientists have found that two non-intoxicating compounds from cannabis, CBD and CBG, may help reduce fat buildup in the liver while improving overall metabolic health. The research shows that these compounds support the liver in

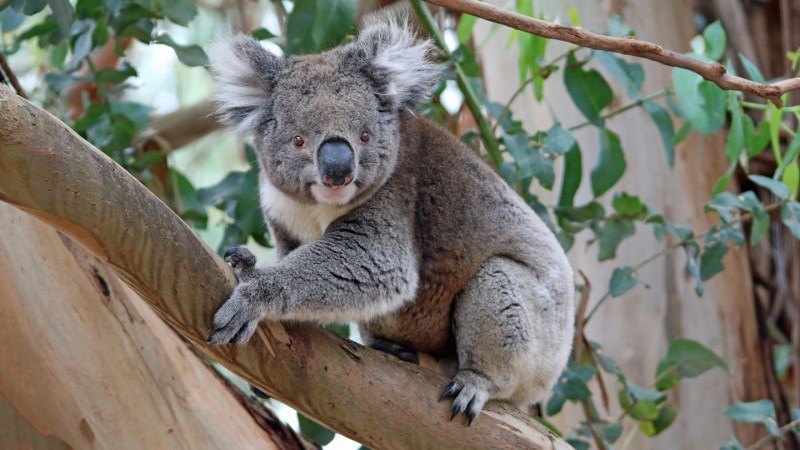
Koalas’ population comeback may be doing more than boosting numbers—it could also be rebuilding their lost genetic diversity. A new genomic study of koalas across Australia suggests that rapid population recovery may help restore genetic diversity that was lost during past declines. Researchers found that when populations grow quickly after a crash, genetic variation can

A large U.S. study suggests that the age and type of groundwater supplying drinking water may be linked to Parkinson’s disease risk. A new preliminary study suggests that the age of the groundwater supplying a community’s drinking water may be linked to the risk of Parkinson’s disease. The research will soon be presented at the
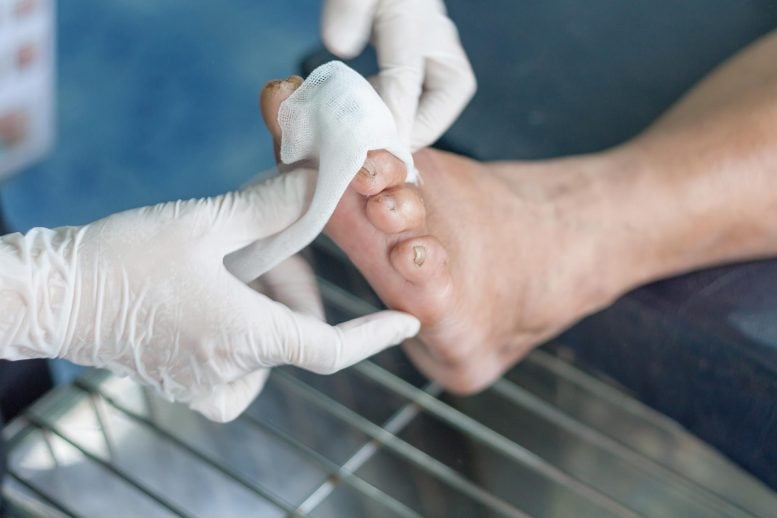
Why do diabetic wounds refuse to heal? A new scientific review highlights how disruptions in the timing and behavior of immune cells may hold the key to understanding this widespread medical challenge. Chronic diabetic ulcers are among the most serious and costly complications associated with diabetes. More than 131 million people around the world are
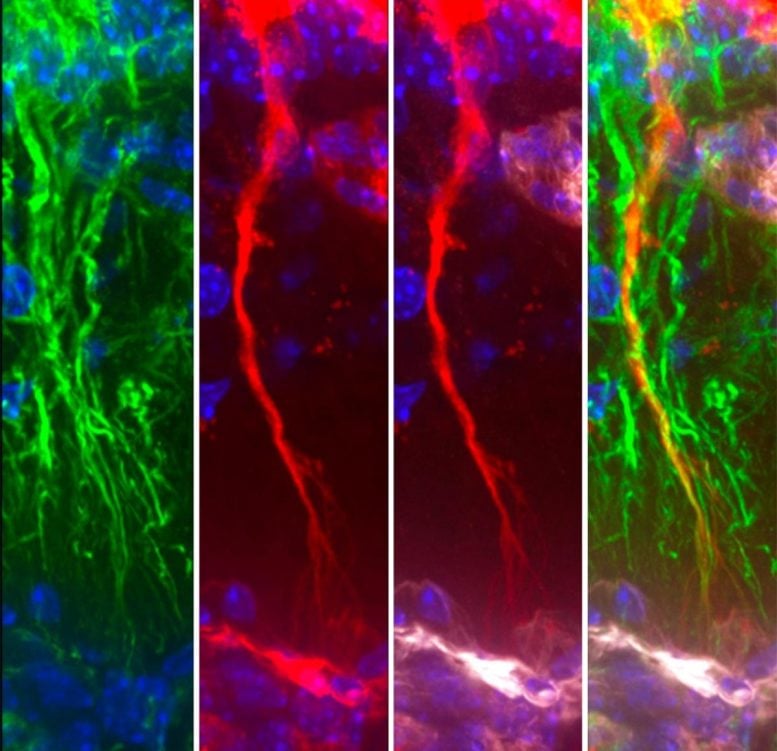
Scientists have identified damaged brain “cleanup” cells called tanycytes as a possible reason toxic tau builds up in Alzheimer’s disease. A buildup of the protein tau in the brain is a defining feature of Alzheimer’s disease. In a study published today (March 5) in the Cell Press journal Cell Press Blue, scientists describe a newly
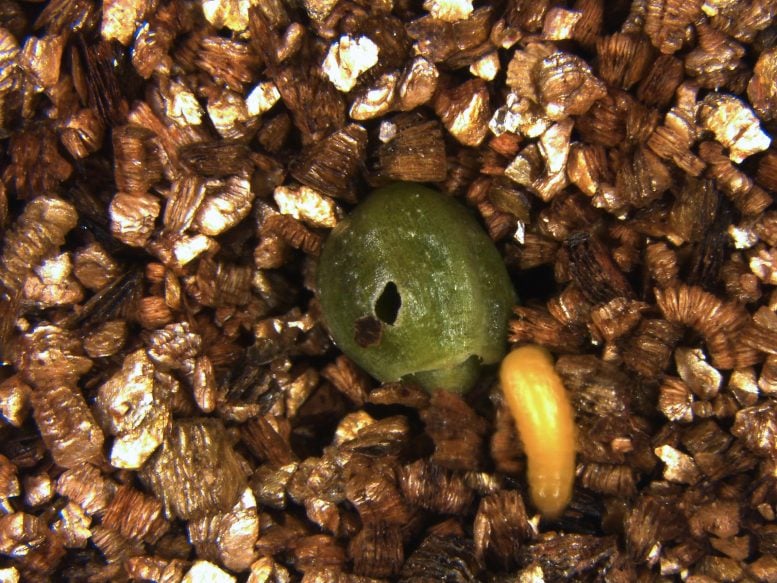

What looks like a plant’s failed fruit may actually be a clever deal that lets both the plant and its pollinating beetles survive. Japanese red elder plants protect their own survival by dropping fruits that contain Heterhelus beetle larvae. Surprisingly, this process also allows the beetle larvae to survive. According to a study from Kobe
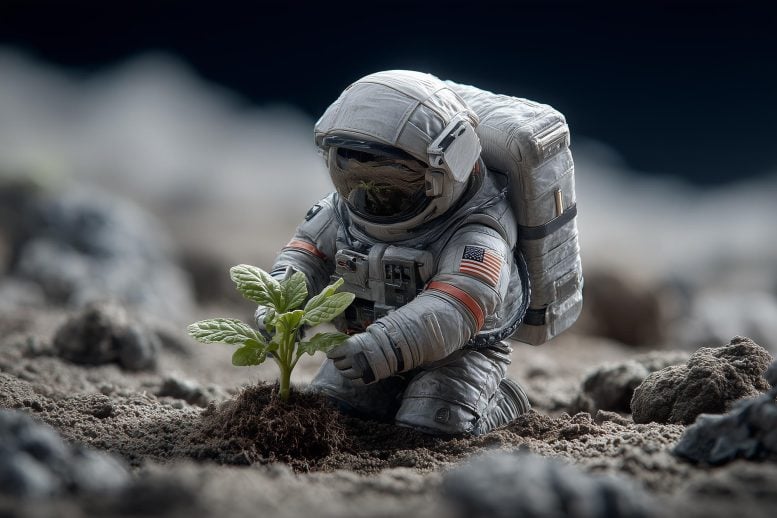

Scientists have grown chickpeas in simulated moon dirt—raising the possibility that future astronauts could one day harvest fresh food on the lunar surface. As NASA prepares for the Artemis II mission and a return to the moon, scientists are exploring a practical question about long-term lunar exploration. What will astronauts eat? New research from The
How does a single cell reliably build one of the most complex structures known in nature? New research suggests the answer may not depend solely on chemical signals, as long assumed. Your brain begins as a single cell. By the end of development, it contains an extraordinarily complex network of roughly 170 billion cells. How
A resurrected ancient enzyme is helping scientists test how reliably Earth’s oldest rocks record signs of life. Scientists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have brought a 3.2 billion-year-old enzyme back to life and tested it inside modern microbes, offering a new way to explore how life began on Earth and how it might be detected
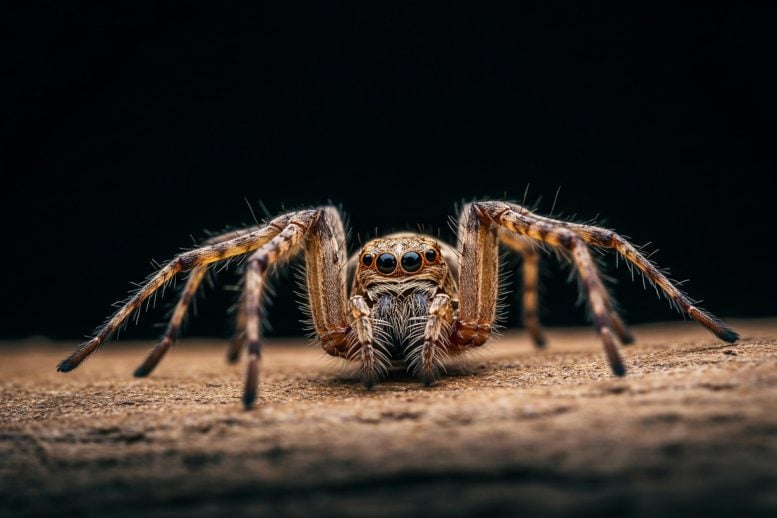

A new study finds that almost 90% of North America’s insects and arachnids have no conservation status at all. Arachnids, including spiders, scorpions, and harvestmen (daddy long-legs), often inspire fear or disgust. Despite their reputation, these animals play an essential role in keeping ecosystems functioning. As global biodiversity declines in what some researchers call the
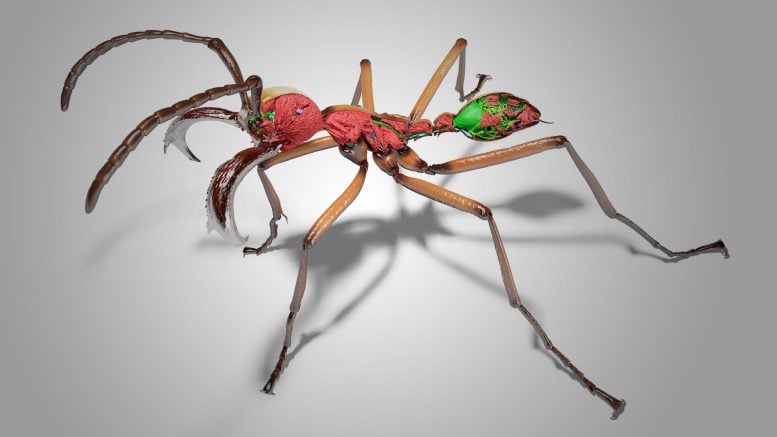

A new high-tech scanning system is rapidly turning thousands of ants into stunning 3D models—building a digital library of Earth’s biodiversity. For more than ten years, Evan Economo’s lab has used micro CT scanners to capture detailed images of insect specimens. These X-ray scans allow scientists to study the shape and structure of insects, an
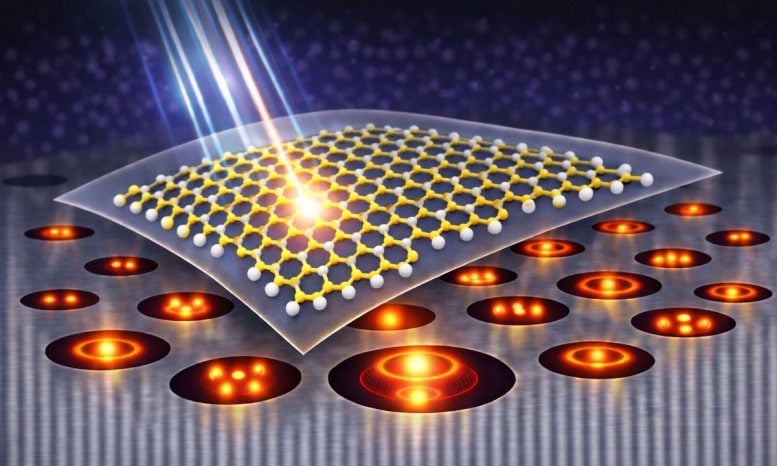
A single layer of atoms may seem too thin to meaningfully interact with light, yet materials like tungsten disulfide are reshaping what is possible in nanophotonics. Researchers have now found a way to dramatically strengthen these interactions. Atomically thin semiconductors such as tungsten disulfide (WS₂) are emerging as key materials for next-generation photonic technologies. Although
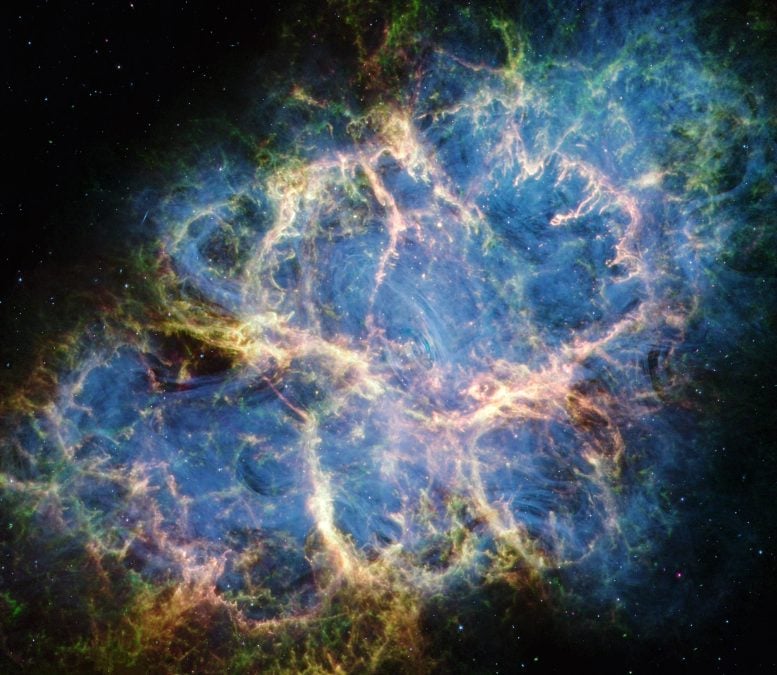

A mysterious striped signal from the Crab Pulsar may finally be explained by a delicate balance between plasma effects and gravitational lensing. For more than 20 years, astronomers have been trying to explain a striking pattern in radio waves coming from the Crab Pulsar. The signal contains bright, evenly spaced stripes that stand out sharply
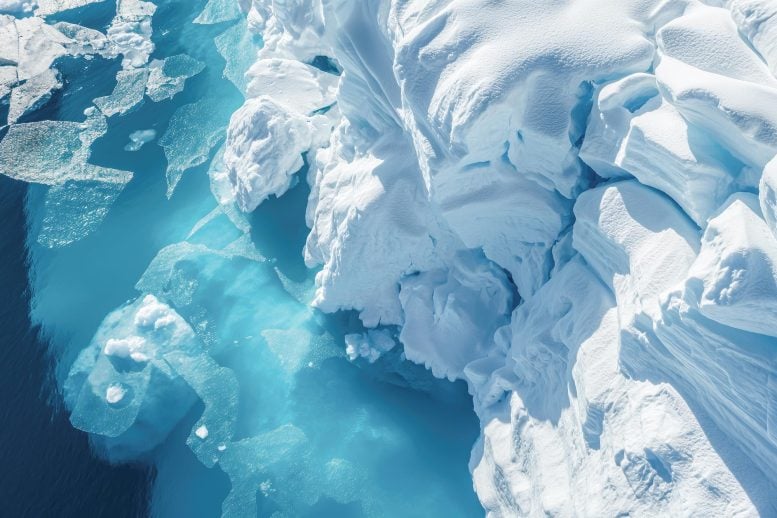

After analyzing three decades of satellite radar data, scientists have created the first continent-wide record of Antarctic grounding line migration. A sweeping 30-year investigation led by glaciologists at the University of California, Irvine has delivered the first continent-wide map showing how Antarctica’s grounding line has shifted over time. By examining three decades of satellite observations,

A newly discovered cancer trick that weakens immunotherapy may be stopped by everyday statins. Cancer immunotherapy has reshaped modern cancer care by activating the body’s own immune defenses to fight tumors. Drugs known as immune checkpoint inhibitors, which target the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, have produced long-lasting responses in some patients and created hope for sustained cancer
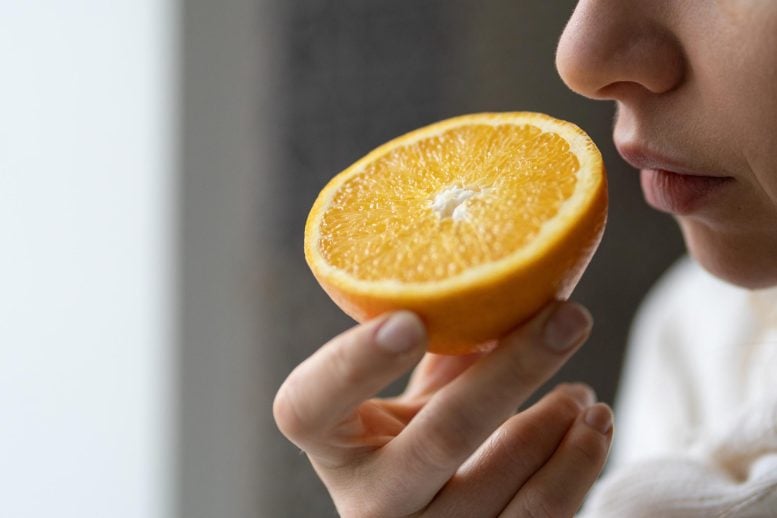

A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help explain why a small number of people continue to struggle with taste loss long after a COVID-19 infection. The study,

Widely used pre-workout supplements may be linked to severely reduced sleep in teens and young adults. A scoop of pre-workout can feel like a shortcut to motivation, especially for teens and young adults juggling school, work, and training. But new findings from the Canadian Study of Adolescent Behaviors suggest that the energy boost may come

A hidden molecular chain reaction in the brain may push key cellular systems into overdrive in autism—and scientists just found a way to switch it off. The brain relies on a constant flow of chemical messages to keep its networks working smoothly. One way to picture this system is like traffic lights in a busy
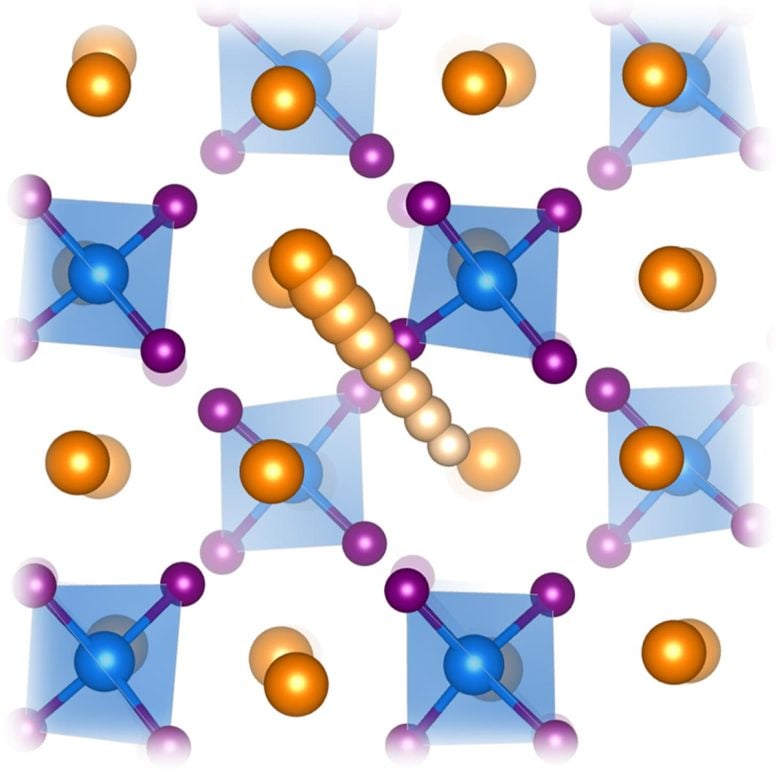
A new AI-driven technique spots the telltale Raman signal of liquid-like ion motion—helping scientists rapidly identify materials for next-generation solid-state batteries. All-solid-state batteries (ASSB) are widely viewed as a safer and potentially more energy-dense alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Their performance relies heavily on how quickly ions can move through solid electrolytes. Finding materials that

A new gene-targeting strategy that boosts a crucial brain protein could pave the way for the first effective treatment for Rett syndrome. Researchers at Texas Children’s Duncan Neurological Research Institute (NRI) and Baylor College of Medicine have identified a possible new strategy for treating Rett syndrome. Their findings, published today (March 4) in Science Translational
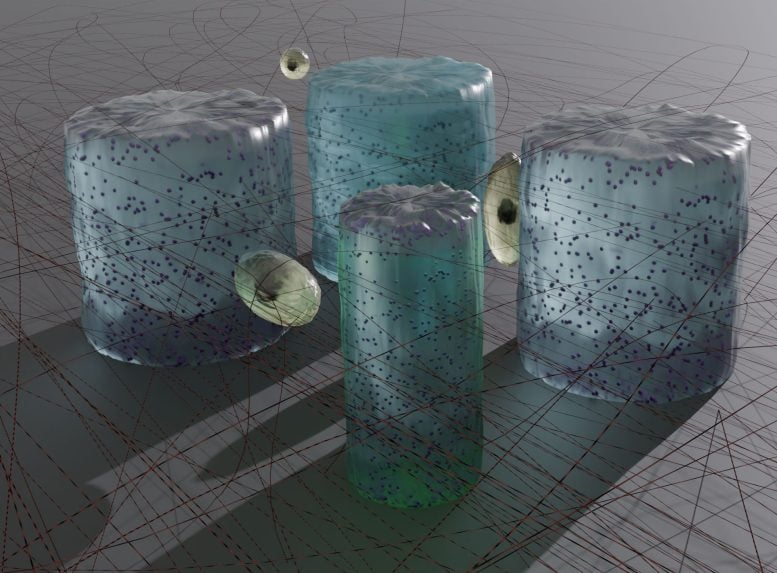
Scientists have engineered a lab-on-a-chip system capable of applying precisely controlled mechanical forces to biological materials that mimic the extracellular matrix. Inside the body, cells are surrounded by intricate three-dimensional scaffolds called the extracellular matrix. The physical interactions between cells and this surrounding structure are essential for many biological functions. Researchers at the Max Planck
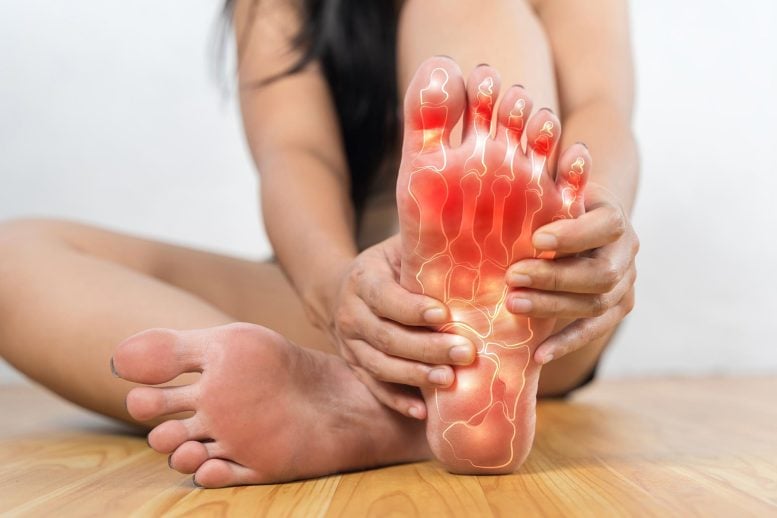
Hormone-regulated immune cells produce IL-10 to resolve pain more effectively in males, offering a potential new target for non-opioid chronic pain treatments. Chronic pain often lingers longer in women than in men. A new study suggests that differences in immune cells known as monocytes could be a key reason. These cells are regulated in part
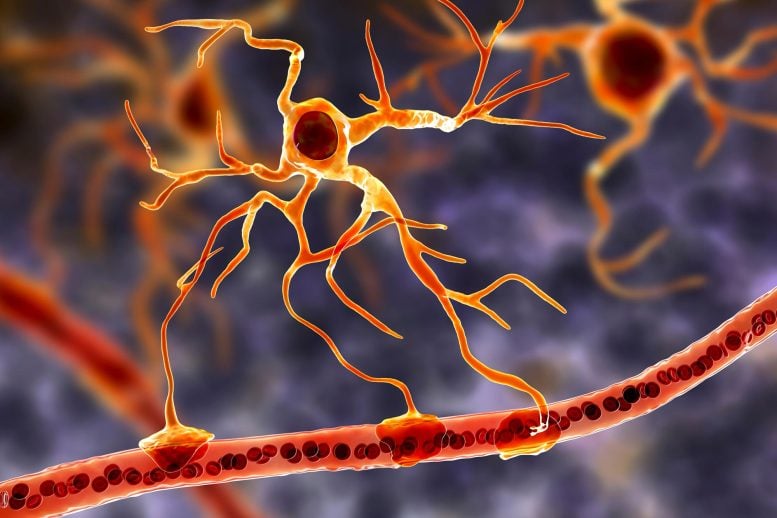
A new study reveals that astrocytes, once dismissed as mere support cells, play a central role in fear memory. Imagine a star-shaped brain cell extending delicate branches that wrap around nearby neurons. This cell is called an astrocyte. For many years, scientists believed astrocytes mainly served as caretakers, helping hold neural networks together and supporting

New research suggests that attention does not remain steady, but instead cycles rhythmically several times per second. Scientists may be closer to understanding why pop-ups and notifications are so hard to ignore. New research suggests that attention does not remain steady. Instead, it fluctuates in a rapid cycle, shifting focus about seven to ten times
RSS Error: A feed could not be found at `https://rss.app/feeds/GivP43K2aZ2AJA3P.xml`; the status code is `402` and content-type is `text/plain; charset=utf-8`
RSS Error: A feed could not be found at `https://rss.app/feeds/APQXK7ILKPjA55YU.xml`; the status code is `402` and content-type is `text/plain; charset=utf-8`
Growing neurons rely on chemical cues to find their targets, but new research shows that the brain’s physical properties help shape those signals. Scientists discovered that tissue stiffness can trigger the production of guidance molecules through a force-sensing protein called Piezo1. This protein not only detects mechanical forces but also helps maintain the structure of brain tissue. The discovery reveals a powerful link between the brain’s physical environment and how…
Tyrannosaurus rex may have taken far longer to grow up than scientists once thought. By analyzing growth rings in fossilized leg bones from 17 tyrannosaur specimens and using new statistical methods, researchers found that the famous predator likely took about 40 years to reach its full size—around eight tons—rather than the previously estimated 25 years.
A sweeping new study of more than 2,000 insect species reveals a troubling reality: many insects may be far less capable of coping with rising temperatures than scientists once hoped. Researchers found that while some species living at higher altitudes can temporarily boost their heat tolerance, many insects in tropical lowlands—where biodiversity is highest—lack this flexibility. Because insects play essential roles as pollinators, decomposers, and predators, their vulnerability could ripple…
Popular weight-loss drugs such as Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro may do more than help people shed pounds. New research suggests these GLP-1 medications could also help protect the heart after a heart attack by restoring blood flow in tiny blood vessels that often remain blocked even after doctors reopen a major artery.
Scientists have uncovered a crucial weakness in the malaria parasite that could open the door to new treatments. Researchers identified a protein called Aurora-related kinase 1 (ARK1) that acts like a traffic controller during the parasite’s unusual cell division process, ensuring its genetic material is properly separated as it multiplies. When scientists switched off ARK1 in laboratory experiments, the parasite could no longer replicate correctly and failed to complete its…
A new experimental drug is showing remarkable promise for children with Dravet syndrome, a severe genetic form of epilepsy. In clinical trials, the treatment zorevunersen cut seizures by as much as 91% while also improving quality of life for many patients. The therapy works by boosting the function of a key gene involved in nerve cell signaling. Encouraging results have led researchers to launch a larger Phase 3 trial.
Returning rescued slow lorises to the wild may sound like a conservation success, but a new study shows it can turn deadly. Researchers tracked nine released animals and found that only two survived, with most killed in territorial attacks by other lorises. Scientists say better planning is essential to ensure wildlife releases actually help endangered species.
Japanese snow monkeys don’t just soak in hot springs to escape the winter chill — their steamy spa sessions may also be reshaping their invisible world. Researchers in Japan found that macaques who regularly bathe show subtle but intriguing differences in lice patterns and gut bacteria compared to those who stay dry. Surprisingly, sharing the hot pools didn’t increase their parasite load, challenging assumptions about disease risk.
Daily aspirin does not reliably prevent bowel cancer in people at average risk, according to a major new review. Any potential protective effect may take more than a decade to appear — if it appears at all — and the evidence for that benefit is weak. In contrast, the risk of serious bleeding begins right away, even with low-dose aspirin. Experts warn that prevention decisions should be individualized, not automatic.
Iron Age teeth from southern Italy have become time capsules, preserving intimate details of childhood and diet. Growth lines in the enamel reveal moments of early-life stress, while hardened plaque holds microscopic remains of cereals, legumes, and fermented foods. The findings suggest a community with diverse food resources and strong Mediterranean connections. Even a small sample offers a striking glimpse into how people lived, grew, and ate nearly three millennia…
Stiff knees and aching hips may seem like an inevitable part of aging, but experts say we’re getting osteoarthritis all wrong. Despite affecting nearly 600 million people worldwide — and potentially a billion by 2050 — the most powerful treatment isn’t surgery or medication. It’s exercise. Movement nourishes cartilage, strengthens muscles, reduces inflammation, and even reshapes the biological processes driving joint damage.
Scientists have used a laser technique to analyze Charles Darwin’s original Galápagos specimens without opening their nearly 200-year-old jars. By shining light through the glass, the method reveals the chemical makeup of the preservation fluids inside. Researchers successfully identified the contents in most samples, offering new clues about historical preservation practices. The breakthrough could help museums protect millions of delicate specimens without risking damage.
Scientists at the University of Tokyo have captured something never seen before: a frame-by-frame view of how electron spins flip inside an antiferromagnet, a material once thought to be magnetically “invisible.” By firing ultrafast electrical pulses into a thin layer of manganese–tin and tracking the response with precisely timed flashes of light, the team uncovered two distinct switching mechanisms. One relies on heat generated by strong currents, while the other…
A sweeping new study reveals that what’s on your plate may directly shape the pesticides circulating in your body. Researchers found that people who eat more fruits and vegetables known to carry higher pesticide residues—such as strawberries, spinach, and bell peppers—also have significantly higher levels of those chemicals in their urine. While produce remains a cornerstone of a healthy diet, the findings highlight how everyday food choices can drive real-world…
An international team combining two major neutrino experiments has uncovered stronger evidence that neutrinos and antimatter don’t behave as perfect mirror images. That subtle difference may hold the key to why the universe didn’t vanish in a flash of self-destruction after the Big Bang.
A famously resilient bacterium may be tough enough to survive one of the most violent events imaginable on Mars. In laboratory experiments designed to mimic the crushing shock of a massive asteroid impact, researchers squeezed Deinococcus radiodurans between steel plates and blasted it with pressures reaching 3 GPa (30,000 times atmospheric pressure). Even under these extreme conditions, a significant portion of the microbes survived.
Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have spotted the most distant “jellyfish galaxy” ever seen — a cosmic oddity streaming long, tentacle-like trails of gas and newborn stars as it speeds through a dense galaxy cluster. The galaxy appears as it was 8.5 billion years ago, revealing that the early universe may have been far more violent than scientists expected.
For decades, scientists have mapped attention, memory, language, and reasoning to separate brain networks — yet one big mystery remained: why does the mind feel like a single, unified system? Researchers at the University of Notre Dame now suggest that intelligence doesn’t live in one “smart” region of the brain at all. Instead, it emerges from how efficiently and flexibly the brain’s many networks communicate and coordinate with each other.
Researchers at the University of Basel and the ETH in Zurich have succeeded in changing the polarity of a special ferromagnet using a laser beam. In the future, this method could be used to create adaptable electronic circuits with light.
In Yellowstone’s wild chess match between wolves and cougars, it turns out the real power play is theft. After tracking nearly a decade of GPS data and thousands of kill sites, researchers found that wolves often muscle in on cougar kills—sometimes even killing the cats—but cougars never return the favor. Instead of fighting back, cougars adapt. As elk numbers dropped, they shifted toward hunting more deer, which they can eat…
When a bone break is too severe to heal on its own, surgeons often rely on grafts or rigid metal implants — but both come with serious drawbacks. Now, researchers at ETH Zurich have created a jelly-like hydrogel that mimics the body’s natural healing process, offering a potentially game-changing alternative. Made of 97% water, this soft material can be laser-printed into intricate bone-like structures at record-breaking speeds, down to details…
Earth’s vertebrate diversity may be far richer than anyone realized. A sweeping analysis of more than 300 studies suggests that for every known fish, bird, reptile, amphibian, or mammal species, there are about two nearly identical “cryptic” species hiding in plain sight—genetically distinct but visually almost impossible to tell apart. Thanks to advances in DNA sequencing, scientists are uncovering these long-separated lineages, some evolving independently for over a million years.
Tiny, tooth-sized fossils have just reshaped the story of our deepest ancestry. Paleontologists have discovered the southernmost remains ever found of Purgatorius—the earliest-known relative of all primates, including humans—in Colorado’s Denver Basin. Previously thought to be confined to Montana and parts of Canada, this shrew-sized, tree-dwelling mammal now appears to have spread southward soon after the asteroid impact that wiped out the dinosaurs.
Polyamines—natural molecules found in every living cell—have become stars in the longevity world for their ability to boost cellular cleanup and support healthy aging. But there’s a dark twist: high levels of these same molecules are consistently seen in cancer, where tumors grow aggressively.
Even in the ultra-dry Atacama Desert, tiny soil-dwelling nematodes are thriving in surprising diversity. Scientists found that biodiversity increases with moisture and altitude shapes which species survive. In the most extreme zones, many nematodes reproduce asexually — a possible survival advantage. The discovery suggests that life in arid regions may be far richer, and more fragile, than once believed.
Icy moons circling the outer planets may be far more dynamic—and explosive—than they appear. New research suggests that when heat from tidal forces melts their ice shells from below, the sudden drop in pressure could cause hidden oceans to boil beneath the surface. On smaller moons like Enceladus, Mimas, and Miranda, this process may help explain strange features such as Enceladus’ tiger stripes and Miranda’s towering cliffs.
As millions turn to ChatGPT and other AI chatbots for therapy-style advice, new research from Brown University raises a serious red flag: even when instructed to act like trained therapists, these systems routinely break core ethical standards of mental health care. In side-by-side evaluations with peer counselors and licensed psychologists, researchers uncovered 15 distinct ethical risks — from mishandling crisis situations and reinforcing harmful beliefs to showing biased responses and…
Why do we tip—even when we know we’ll never see the server again? New research suggests it’s not just about rewarding good service, but about social pressure. Some people tip out of genuine appreciation, while others simply follow the norm. But here’s the twist: those who truly value great service tend to tip more than average, and everyone else adjusts upward to match them.
NYU researchers have found a way to use light to control how microscopic particles assemble into crystals, effectively turning illumination into a tool for shaping matter. By adding light-sensitive molecules to a liquid filled with tiny particles, they can adjust how strongly the particles attract or repel one another simply by changing the light’s intensity or pattern. This allows them to trigger crystals to form, dissolve, or even be reshaped…
For the first time ever, scientists have uncovered a vast field of tektites in Brazil — mysterious glassy fragments forged when a powerful extraterrestrial object slammed into Earth about 6.3 million years ago. Named “geraisites” after Minas Gerais, where they were first found, these dark, aerodynamic droplets of natural glass stretch across more than 900 kilometers and may mark one of South America’s most significant ancient impact events.
Scientists in Brazil have transformed cocoa waste into a functional chocolate-infused honey packed with antioxidants and natural stimulants. Using ultrasound waves, they enhanced honey’s ability to pull beneficial compounds from cocoa shells—no synthetic solvents required. The process is considered green and sustainable, and the product could find its way into gourmet foods and cosmetics.
Scientists at Rice University have produced the first full, dye-free molecular atlas of an Alzheimer’s brain. By combining laser-based imaging with machine learning, they uncovered chemical changes that spread unevenly across the brain and extend beyond amyloid plaques. Key memory regions showed major shifts in cholesterol and energy-related molecules. The findings hint that Alzheimer’s is a whole-brain metabolic disruption—not just a protein problem.
Astronomers have long known the universe is expanding—but exactly how fast remains one of the biggest mysteries in cosmology. Different techniques for measuring the Hubble constant stubbornly disagree, creating the so-called “Hubble tension.” Now researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Chicago have unveiled a bold new way to weigh in on the debate using gravitational waves—the faint ripples in spacetime produced by colliding black holes.
Scientists have pulled off a feat long considered out of reach: getting light to mimic the famous quantum Hall effect. In their experiment, photons drift sideways in perfectly defined, quantized steps—just like electrons do in powerful magnetic fields. Because these steps depend only on nature’s fundamental constants, they could become a new gold standard for ultra-precise measurements. The discovery also hints at tougher, more reliable quantum photonic technologies.
Jupiter’s icy moons may have been seeded with the chemical ingredients for life from the very beginning. An international team of scientists modeled how complex organic molecules—essential building blocks for biology—could have formed in the swirling disk of gas and dust around the young Sun and later been carried into Jupiter’s own moon-forming disk. Their results suggest that up to half of the icy material that built moons like Europa,…
Drug-resistant bacteria are becoming harder to treat, pushing scientists to look for new antibiotic targets. Researchers have now discovered that several unrelated viruses disable a key bacterial protein called MurJ, which is essential for building the bacterial cell wall. High-resolution imaging shows these viral proteins lock MurJ into a single position, stopping cell wall construction and leading to bacterial death.
Scientists have built a massive cellular atlas showing how aging reshapes the body across 21 organs. Studying nearly 7 million cells, they found that aging starts earlier than expected and unfolds in a coordinated way throughout the body. About a quarter of cell types change in number over time, and many of these shifts differ between males and females. The research also highlights shared genetic “hotspots” that could become targets…
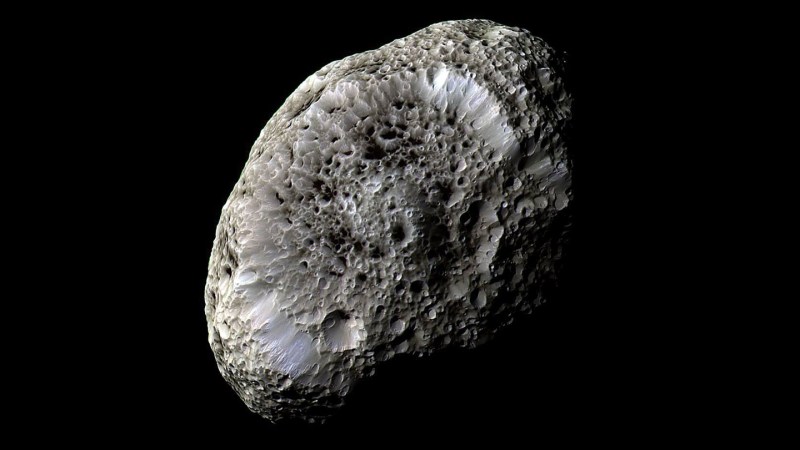
Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, may have been born in a colossal cosmic crash. New research suggests Titan formed when two older moons slammed together hundreds of millions of years ago—an event so violent it reshaped Saturn’s entire moon system and may have indirectly sparked the formation of its iconic rings. Clues come from Titan’s unusual orbit, its surprisingly smooth surface, and the strange behavior of the tumbling moon Hyperion.
Scientists at Texas A&M are turning an everyday pick-me-up into a high-tech medical switch. By combining caffeine with CRISPR gene editing, researchers have created a system that allows cells to be programmed in advance — and then activated simply by consuming a small dose of caffeine from coffee, chocolate, or soda. The approach, known as chemogenetics, lets scientists precisely turn gene-editing activity on and off inside targeted cells, including powerful…
Astronomers have spotted what may be one of the universe’s earliest barred spiral galaxies — a striking cosmic structure forming just 2 billion years after the Big Bang. The galaxy, COSMOS-74706, dates back about 11.5 billion years and contains a stellar bar, a bright, linear band of stars and gas stretching across its center, similar to the one in our own Milky Way.
Scientists have uncovered a surprising new way that giant embryonic cells divide—without relying on the classic “purse-string” ring long thought essential for splitting a cell in two. Studying zebrafish embryos, researchers found that instead of forming a fully closed contractile ring, cells use a clever “mechanical ratchet” system.
Sponges may be ancient, but their timeline has been murky. New research suggests the earliest sponges were soft and skeleton-free, explaining why their fossils don’t appear until much later. By analyzing hundreds of genes and modeling how skeletons evolved, scientists found that mineralized spicules arose separately in different sponge lineages. The discovery rewrites the story of how the first reef-building animals—and possibly the first animals of all—emerged.
Scientists at UC Berkeley have discovered a microbe that bends one of biology’s most sacred rules. Instead of treating a specific three-letter DNA code as a clear “stop” signal, this methane-producing archaeon sometimes reads it as a green light—adding an unusual amino acid and continuing to build the protein. The result is a kind of genetic coin flip: two different proteins can emerge from the same code, influenced partly by…
Scientists at MIT have found compelling chemical evidence that Earth’s earliest animals were likely ancient sea sponges. Hidden inside rocks over 541 million years old are rare molecular “fingerprints” that match compounds made by modern demosponges. After testing rocks, living sponges, and lab-made molecules, researchers confirmed the signals came from life — not geology. The discovery suggests sponges were thriving in the oceans well before most other animal groups appeared.
Scientists have unveiled a breakthrough way to turn natural gas—long burned as fuel—into valuable chemical building blocks for medicines and other high-demand products. By designing a clever iron-based catalyst powered by LED light, researchers managed to activate stubborn molecules like methane and transform them into complex compounds, even creating the hormone therapy drug dimestrol directly from methane for the first time.
For decades, scientists believed a fertilized egg’s DNA began as a shapeless mass, only organizing itself once the embryo switched on its genes. But new research reveals that the genome is already carefully arranged in three dimensions long before that critical activation step, known as Zygotic Genome Activation. Using a powerful new method called Pico-C, researchers captured this hidden DNA architecture in unprecedented detail, showing that a complex scaffold is…
Researchers at Nagoya University have created a more efficient iron-based photocatalyst that could reduce the need for rare and expensive metals in advanced chemistry. Unlike earlier designs, the new catalyst uses far fewer costly chiral ligands while still precisely controlling the three dimensional structure of molecules.
Baby dinosaurs weren’t coddled like lion cubs or elephant calves—they were more like prehistoric latchkey kids. New research suggests that young dinosaurs quickly struck out on their own, forming kid-only groups and surviving without much parental help, while their massive parents lived entirely different lives. Because juveniles and adults ate different foods, faced different predators, and moved through different parts of the landscape, they may have functioned almost like separate…
The Old Irish Goat isn’t just part of folklore — it’s genetically linked to goats that lived in Ireland 3,000 years ago. Scientists analyzed ancient remains and discovered that today’s rare breed shares its strongest DNA ties with Late Bronze Age animals. The finding suggests an unbroken Irish lineage stretching back millennia. It also adds urgency to protecting this critically endangered survivor of Ireland’s agricultural past.
“Forever chemicals” known as PFAS have quietly infiltrated everything from nonstick pans to food packaging—and now new research suggests some of them may be speeding up the aging process itself. In a nationally representative U.S. study, two lesser-known PFAS compounds, PFNA and PFOSA, were found in 95% of participants and strongly linked to faster biological aging in men aged 50 to 64.
Using the NIRSpec data, planetary scientists measured the physical properties of the auroral footprints of Jupiter’s two innermost Galilean moons, Io and Europa, including the local temperature and ionospheric density, in the near-infrared. The post Webb Captures Io’s and Europa’s Auroral Footprints in Jupiter’s Atmosphere appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
An international team of archaeologists has examined a total of 85 pottery sherds with substantial amounts of foodcrusts from 13 archaeological sites across Northern and Eastern Europe i dating from the 6th to the 3rd millennium BCE. The post Neolithic Europeans Had Surprisingly Complex Cuisine, Archaeologists Say appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Using spectral data from the Hobby-Eberly Telescope at McDonald Observatory, astronomers have produced the most detailed 3D map yet of faint cosmic structures from 9-11 billion years ago, revealing galaxies and intergalactic gas once invisible to telescopes. The post Astronomers Find Hidden Structures in Early Universe appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
New research shows that Deinococcus radiodurans has outstanding ability to survive the extreme transient pressures associated with impact-induced ejection from Mars. The post Extremophile Bacteria May Hitch Rides on Asteroid Fragments appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
New images from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and ESA’s Euclid mission have revealed the complex, multi-shell structure of the extraordinary planetary nebula NGC 6543, also known as the Cat’s Eye Nebula. The post Hubble and Euclid Telescopes Highlight Hidden Complexity of Cat’s Eye Nebula appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
The newly-discovered minuscule fossils of Purgatorius -- a shrew-sized mammal considered the earliest known relative of all primates, including humans, and long thought to be confined to northern North America -- extend the known range of this mammal hundreds of km south. The post Southernmost Fossils of Earliest Primate Relative Unearthed in Colorado appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
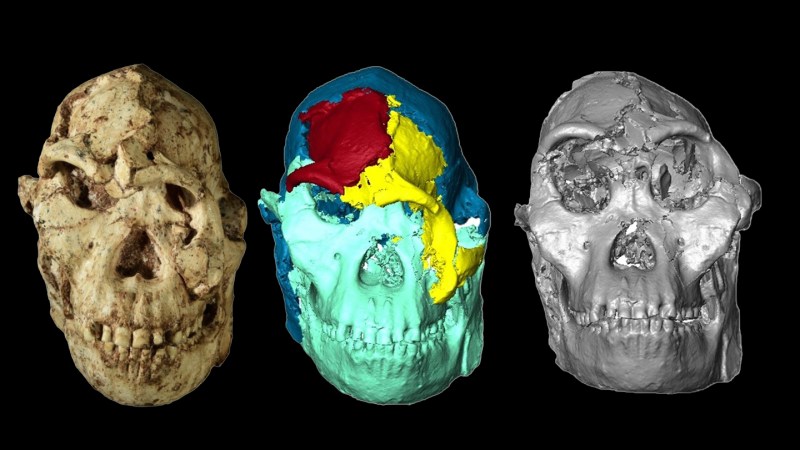
Beyond their value for classification and evolutionary relationships, changes in the size and shape of the hominin face through time can reflect important functional adaptations. The post Scientists Digitally Reconstruct Face of ‘Little Foot’ appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Paleontologists at the University of Toronto Mississauga have found dozens of tooth marks on the fossilized bones of three juveniles of Diadectes, one of the earliest large plant-eating vertebrates to walk on land. The post 280-Million-Year-Old Fossil Provides Earliest Direct Evidence of Land Predators Attacking Herbivores appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Paleontologists have described the youngest example yet of a pachycephalosaur body, offering a look at how these dinosaurs grew and moved during their first months of life. The post Rare Fossil of Baby Dome-Headed Dinosaur Unearthed in Canada appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
New research from the University of Kansas untangles a decades-old astrophysical puzzle, showing how competing forces -- gravity’s pull and magnetospheric plasma -- split the radio emissions emanating from the Crab Pulsar, the remnant of a supernova observed by ancient astronomers in 1054 CE, into perfectly spaced ‘stripes.’ The post Astronomer Deciphers Crab Pulsar’s Zebra Stripes appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Using the High Acuity Wide-field K-band Imager (HAWK-I) on ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), astronomers have captured a new image of the emission nebula RCW 36, highlighting the luminous cradle of newborn stars and substellar objects known as brown dwarfs. The post VLT Focuses on Brown Dwarfs and Infant Stars in RCW 36 appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Prehistoric humans and Neanderthals didn’t just interbreed, they did so with a consistent sex bias, as male Neanderthals and female modern humans mated more often. The post Study: Ancient Mating Preferences Helped Shape Human Genome appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Planetary scientsts from the United States, Europe and China have used the Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) onboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft to map detailed patch structures in Ganymede’s aurorae that parallel those seen on Earth. The post Ganymede’s Auroral Patches Reveal Shared Physics with Earth’s Aurorae appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
The JANUS science camera aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) has captured new images of the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS. The post Juice Spies Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
The unmatched sensitivity of the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope in both near- and mid-infrared light sheds new light on PMR 1, a little-studied nebula in the constellation of Vela. The post Webb’s Infrared Vision Reveals Planetary Nebula that Looks Strikingly Like Celestial Brain appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Fossils trapped in amber aren’t just beautiful, they may preserve real ecological interactions, including possible parasitism or commensal relationships between ants and mites, as revealed by a new, cutting-edge morphological study of six specimens of Baltic, Dominican and Burmese amber. The post Fossil Amber Preserves Ecological Interactions between Ancient Ants and Other Organisms appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
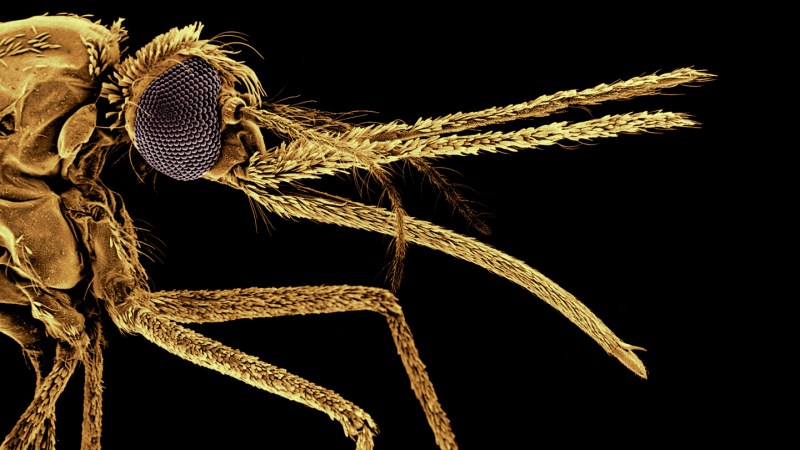
The ancestors of today’s malaria-spreading mosquitoes in the Anopheles leucosphyrus (Leucosphyrus) group may have shifted to feeding on humans around 1.8 million years ago, coinciding with the arrival of Homo erectus in Southeast Asia. The post Arrival of Homo erectus in Southeast Asia Changed Mosquito Menu, New Study Suggests appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Pennsylvania State University researchers have directly observed and measured an electrical phenomenon called corona on sweetgum, loblolly pine and other tree species under thunderstorms in several U.S. states. The post Scientists Observe Electrical Discharges on Trees under Thunderstorms appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
A remarkably complete skeleton of the alvarezsauroid dinosaur species Alnashetri cerropoliciensis from Patagonia, Argentina, as well as two alvarezsauroid specimens from the northern hemisphere reveal how the once-mysterious lineage of theropod dinosaurs evolved and spread before continents drifted apart. The post 90-Million-Year-Old Patagonian Fossil Reveals Missing Chapter in Evolution of Alvarezsauroid Dinosaurs appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
With the record-setting image from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have mapped the molecular heart of our Milky Way Galaxy in breathtaking detail. The post ALMA Produces Largest and Most Detailed Image Ever Taken of Milky Way’s Center appeared first on Sci.News: Breaking Science News.
Russia is attacking Ukraine with Shahed-136-type drones every night now. Ukraine has put up additional air defences in
Nuclear bomb is a weapon that employs the energy from a nuclear reaction. Resulting radiation and the fallout
Russia’s main air-defence systems are S-300 and S-400. Those are expensive missile systems, capable of engaging all kinds
More accurately predicting periods of increased hurricane activity weeks in advance may become possible due to new research
Researchers at ETH Zurich and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems have developed a robotic leg with
AstraZeneca has entered into a collaboration with biotech firm Immunai Inc., investing $18 million to utilize Immunai’s advanced
Astronomy has always relied on light to convey information about the universe. But capturing photons — such as
Meta Platforms, formerly Facebook, showcased its new augmented reality (AR) glasses prototype, Orion, during its annual Connect conference.
Nebius Group, an Amsterdam-based tech company born from the division of assets previously owned by Russian technology giant
In the desert of Texas, an innovative construction project is unfolding—one that uses a crane-sized 3D printer to
PayPal Holdings announced a major development on Wednesday, allowing U.S. merchants to buy, hold, and sell cryptocurrency directly
Russia has covertly established a weapons program in China to create long-range attack drones for use in the
The Sukhoi Su-57 is a Russian fifth-generation fighter jet, built as a response to the American F-22 Raptor.
Alphabet’s Google is partnering with Volkswagen to provide cutting-edge artificial intelligence capabilities for an in-app assistant designed specifically
Stability AI, an emerging leader in artificial intelligence, announced on Tuesday that renowned filmmaker James Cameron, director of
Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian denies reports that Iran has transferred a large quantity of Fath 360 short-range ballistic
Russia has emerged as the primary foreign actor using artificial intelligence (AI) to sway the U.S. presidential election,
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has announced plans to launch approximately five uncrewed Starship missions to Mars within the